Every night, millions of people perform the same ritual: fumbling in the dark for a charging cable, trying to plug it in the right way, and hoping the connection holds through the night. Yet increasingly, people are simply placing their phones on a pad and walking away. No cables, no ports, no hassle. Wireless charging has grown from a novelty to a standard feature, with over 1 billion devices now supporting it. But how does electricity jump through thin air? And why does your phone need to be positioned just right?
The technology behind wireless charging isn’t magic – it’s physics that’s been understood for over 100 years. Michael Faraday discovered the principles in 1831, Nikola Tesla experimented with it in the 1890s, and now it’s in your pocket. This guide explains exactly how wireless charging works, why it sometimes doesn’t, and everything you need to know about using and choosing wireless chargers.
The Science Behind Wireless Charging
The Basic Principle: Electromagnetic Induction
Wireless charging works through a principle called electromagnetic induction – the same physics that powers electric motors and transformers. Here’s what actually happens when you place your phone on a charging pad:
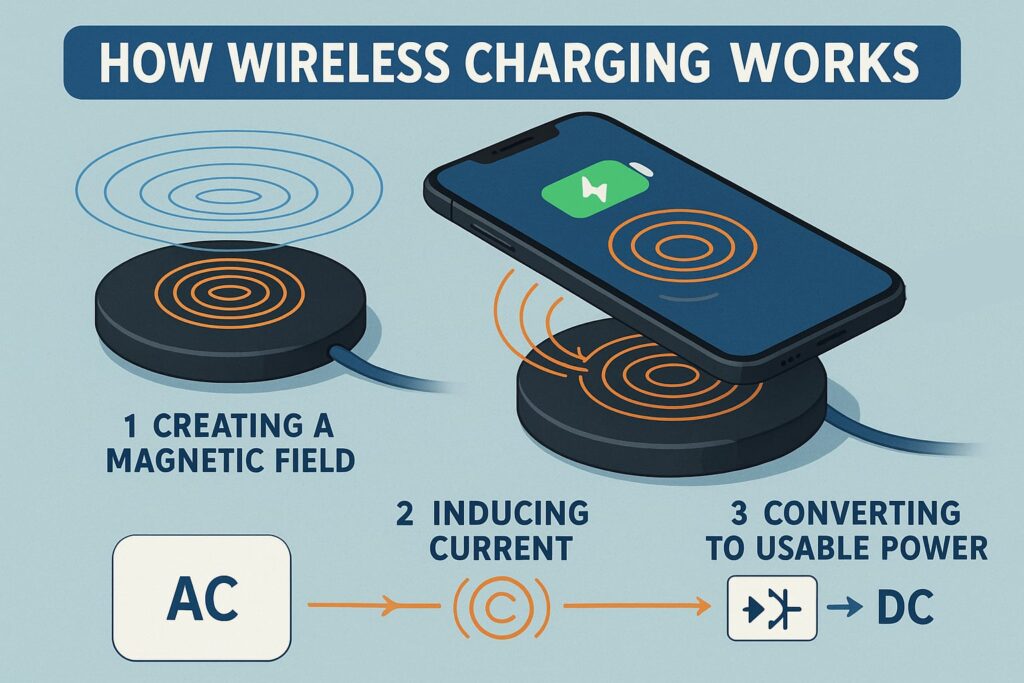
Step 1: Creating a Magnetic Field The charging pad contains a coil of wire. When electricity flows through this coil, it creates a magnetic field around it. This field extends beyond the pad itself, reaching into the space above it.
Step 2: Inducing Current Your phone contains its own coil of wire. When this coil enters the magnetic field from the charging pad, the changing magnetic field induces an electrical current in your phone’s coil. It’s like an invisible connection between the two coils.
Step 3: Converting to Usable Power The induced alternating current (AC) in your phone gets converted to direct current (DC) through a rectifier. This DC power then charges your battery, just like a traditional charger would.
The Key Requirements:
- Two coils (one transmitting, one receiving)
- Alternating current in the transmitter
- Close proximity between coils
- Proper alignment for efficiency
Why Distance Matters So Much
The strength of the magnetic field decreases dramatically with distance. This follows the inverse square law – doubling the distance reduces the power to one-quarter. That’s why:
- Your phone needs to be directly on the pad
- Even a thick case can slow charging
- Slight misalignment reduces efficiency
- Metal objects between coils block charging completely
Real-World Impact:
- 0mm gap: 80-90% efficiency
- 5mm gap: 60-70% efficiency
- 10mm gap: 30-40% efficiency
- 15mm gap: Often won’t charge at all
Types of Wireless Charging Technologies
1. Inductive Charging (Qi Standard)
How It Works: Uses tightly coupled electromagnetic induction between two coils.
Characteristics:
- Range: 5-10mm maximum
- Efficiency: 70-80% typically
- Power: 5W to 15W standard, up to 50W possible
- Alignment: Requires precise positioning
Where You’ll Find It:
- Smartphones (iPhone, Samsung, Google)
- Earbuds (AirPods, Galaxy Buds)
- Smartwatches (Apple Watch, Galaxy Watch)
- Electric toothbrushes
- Some laptops and tablets
Advantages:
- Widely adopted standard
- Relatively efficient
- Safe and proven
- Cost-effective
Disadvantages:
- Very short range
- Requires alignment
- Generates heat
- Slower than wired charging
2. Resonant Charging
How It Works: Uses loosely coupled resonant induction, where both coils are tuned to the same frequency.
Characteristics:
- Range: Several centimeters to meters
- Efficiency: 40-60% at distance
- Power: Variable, can be high
- Alignment: More flexible
Where You’ll Find It:
- Some electric vehicle charging
- Experimental phone chargers
- Medical implants
- Industrial applications
Advantages:
- Greater distance possible
- Multiple devices simultaneously
- Less alignment sensitivity
- Through-surface charging
Disadvantages:
- Lower efficiency
- More complex technology
- Higher cost
- Limited consumer adoption
3. Radio Frequency (RF) Charging
How It Works: Converts electricity to radio waves, transmits them, then converts back to electricity.
Characteristics:
- Range: Several meters possible
- Efficiency: Very low (under 10%)
- Power: Milliwatts to watts
- Alignment: Not required
Where You’ll Find It:
- RFID tags
- Some IoT sensors
- Experimental systems
- Medical devices
Advantages:
- Long range
- No alignment needed
- True wireless freedom
- Multiple devices
Disadvantages:
- Extremely inefficient
- Very slow charging
- Regulatory limitations
- Health concerns at high power
The Qi Standard: How Most Wireless Chargers Work
Qi (pronounced “chee”) is the dominant wireless charging standard, developed by the Wireless Power Consortium. Understanding Qi helps you understand most wireless chargers on the market.
Qi Charging Process
1. Detection Phase
- Charger sends a ping every few seconds
- Looks for Qi-compatible devices
- Uses minimal power during detection
2. Identification Phase
- Device responds with identification
- Communicates power requirements
- Negotiates charging parameters
3. Power Transfer Phase
- Charging begins at negotiated rate
- Continuous communication maintains efficiency
- Adjusts power based on device needs
4. End of Charge
- Device signals when full
- Charger reduces to trickle charge
- Maintains battery without overcharging
Qi Power Profiles
Basic Power Profile (BPP):
- 5W maximum power
- Original Qi standard
- Slowest charging speed
- Most compatible
Extended Power Profile (EPP):
- 15W maximum power
- Faster charging
- Better efficiency
- Requires compatible devices
Proprietary Fast Charging:
- Samsung: Up to 15W
- Apple: 7.5W (iPhone), 15W (MagSafe)
- OnePlus: 50W (proprietary)
- Xiaomi: 80W (proprietary)
Foreign Object Detection (FOD)
Qi chargers can detect metal objects that shouldn’t be charged:
How FOD Works:
- Measures power sent vs. received
- Detects unusual power loss
- Stops charging if foreign object detected
- Prevents heating of metal objects
Why It Matters:
- Prevents keys from heating up
- Protects credit cards
- Avoids safety hazards
- Maintains efficiency
Real-World Performance: What to Actually Expect
Charging Speed Comparison
iPhone 15 Pro (Example):
- Wired (USB-C PD): 0-50% in 30 minutes
- MagSafe (15W): 0-50% in 60 minutes
- Qi Wireless (7.5W): 0-50% in 90 minutes
- Basic Qi (5W): 0-50% in 120 minutes
Samsung Galaxy S24 (Example):
- Wired (45W): 0-50% in 25 minutes
- Fast Wireless (15W): 0-50% in 55 minutes
- Standard Wireless (10W): 0-50% in 75 minutes
- Basic Qi (5W): 0-50% in 110 minutes
Efficiency and Heat Generation
Where Power Goes:
- 70-80%: Actually charges battery
- 15-20%: Heat generation
- 5-10%: Circuit losses
Heat Impact:
- Reduces charging speed
- Can trigger thermal throttling
- Affects battery longevity
- Worse in summer/hot environments
Managing Heat:
- Use chargers with cooling fans
- Remove thick cases while charging
- Avoid charging in direct sunlight
- Use lower power settings overnight
Real Usage Scenarios
Overnight Charging:
- Speed doesn’t matter
- Convenience is key
- Lower power reduces heat
- Better for battery health
Desktop Charging:
- Constant top-ups
- Maintains 80-100% charge
- Convenient placement
- Reduces port wear
Car Charging:
- Often slower due to heat
- Alignment can be tricky
- Good for navigation use
- Prevents cable tangling
Choosing the Right Wireless Charger
Types of Wireless Chargers
1. Flat Charging Pads
Price Range: $10-50
Best For:
- Nightstands
- Desks
- Single device charging
- Minimal footprint
Pros:
- Affordable
- Simple design
- Widely available
- Reliable
Cons:
- Can’t use phone while charging easily
- Requires precise placement
- Only one device
- No viewing angle
2. Angled Charging Stands
Price Range: $15-70
Best For:
- Desks
- Video calls
- Watching content
- Face ID/unlock
Pros:
- Phone usable while charging
- Better viewing angle
- Often faster charging
- More stable
Cons:
- Larger footprint
- More expensive
- May not work with all cases
- Fixed angle usually
3. Multi-Device Chargers
Price Range: $30-150
Best For:
- Families
- Multiple devices
- Travel (some models)
- Decluttering
Pros:
- Charge everything at once
- Single cable/outlet
- Organized appearance
- Often includes watch charger
Cons:
- Expensive
- Large footprint
- Slower charging sometimes
- All devices must be Qi compatible
4. Portable Power Banks
Price Range: $25-80
Best For:
- Travel
- Emergency charging
- Outdoor activities
- Cable-free backup
Pros:
- True portability
- No outlet needed
- Often includes wired option
- Magnetic attachment (some)
Cons:
- Heavier than regular power banks
- Less efficient
- More expensive
- Needs recharging itself
5. Car Wireless Chargers
Price Range: $20-60
Best For:
- Daily commutes
- Navigation use
- Ride-share drivers
- Cable-free convenience
Pros:
- Hands-free mounting
- Automatic alignment
- One-handed operation
- Reduces cable wear
Cons:
- Slower charging
- Heat issues in summer
- May not fit all phones
- Vibration can affect alignment
Key Features to Consider
Power Output:
- 5W: Basic, slow, universal
- 7.5W: iPhone standard
- 10W: Android standard
- 15W: Fast wireless
- 20W+: Proprietary fast charging
Coil Configuration:
- Single coil: Requires precise alignment
- Double coil: More forgiving placement
- Triple coil: Best flexibility
- Array: Full surface charging
Safety Features:
- Over-voltage protection
- Over-current protection
- Temperature control
- Foreign object detection
- Short circuit protection
Build Quality Indicators:
- Weight (heavier often better)
- Non-slip surface
- Quality USB cable included
- Brand reputation
- Certification marks
Setting Up and Optimizing Wireless Charging
Initial Setup
Step 1: Choose Location
- Stable, flat surface
- Away from heat sources
- Accessible power outlet
- Away from magnetic items
Step 2: Connect Power
- Use included adapter when possible
- Ensure adequate wattage
- Quality USB cable matters
- Avoid daisy-chaining
Step 3: Test Positioning
- Find the sweet spot
- Mark optimal position
- Test with your case on
- Verify charging indicator
Optimizing Charging Speed
Use the Right Adapter:
- 5W charger needs 10W adapter
- 15W charger needs 20W+ adapter
- Quick Charge or PD compatible
- Original manufacturer preferred
Positioning Tips:
- Center phone on pad
- Look for alignment guides
- Listen for charging confirmation
- Check charging animation
Case Considerations:
- Under 3mm thickness ideal
- Remove metal attachments
- Avoid wallet cases
- Consider MagSafe/magnetic cases
Troubleshooting Common Issues
Phone Not Charging:
Possible Causes:
- Misalignment
- Case too thick
- Metal in case
- Insufficient power
- Incompatible charger
Solutions:
- Reposition phone
- Remove case
- Check for metal objects
- Try different adapter
- Verify Qi compatibility
Charging Starts and Stops:
Possible Causes:
- Overheating
- Poor connection
- Defective charger
- Software issue
- Foreign object detected
Solutions:
- Let devices cool
- Clean charging surfaces
- Update phone software
- Remove nearby metal
- Try different charger
Slow Charging:
Possible Causes:
- Low power adapter
- Background apps
- Hot environment
- Thick case
- Wrong charger type
Solutions:
- Use higher wattage adapter
- Close unnecessary apps
- Move to cooler location
- Remove or change case
- Verify fast charging compatibility
The Pros and Cons of Wireless Charging
Advantages
Convenience:
- No cable fumbling
- One-handed operation
- Easy placement in dark
- No port wear
- Cleaner desk/nightstand
Durability:
- No port damage
- No cable fraying
- Waterproofing maintained
- Less mechanical stress
- Longer device lifespan
Universal Compatibility:
- One charger for many devices
- Cross-brand compatibility
- Future-proof investment
- Travel simplification
- Family sharing
Safety:
- No exposed contacts
- Automatic shutoff
- Lower voltage at surface
- Child-safe
- No electrocution risk
Disadvantages
Speed:
- 30-50% slower typically
- Heat throttling common
- Distance sensitive
- Efficiency losses
- Not ideal for quick top-ups
Cost:
- More expensive than cables
- Need multiple chargers
- Higher electricity use
- Replacement costs
- Adapter requirements
Limitations:
- Can’t use phone easily
- Position dependent
- Case restrictions
- Metal interference
- Size constraints
Efficiency:
- 20-30% power loss
- Heat generation
- Higher electricity bills
- Environmental impact
- Battery stress from heat
Future of Wireless Charging
Near-Term Developments (2024-2026)
Faster Charging:
- 30W standard wireless
- 100W+ proprietary systems
- Better heat management
- Improved efficiency
Longer Range:
- Over-desk charging
- Through-surface charging
- Multi-centimeter range
- Room-scale experiments
Integration:
- Built into furniture
- Car integration standard
- Public charging spots
- Laptop wireless charging
Medium-Term Possibilities (2026-2030)
True Wireless Power:
- Meter-range charging
- Multiple device support
- Beam-forming technology
- Smart power routing
Efficiency Improvements:
- 90%+ efficiency
- Minimal heat generation
- Adaptive frequency
- AI-optimized charging
New Applications:
- Wireless powered IoT
- Medical implants
- Electric vehicle charging
- Drone charging pads
Long-Term Vision (2030+)
Ubiquitous Power:
- Room-scale wireless power
- No battery anxiety
- Continuous charging
- Power as a service
Technical Breakthroughs:
- Near 100% efficiency
- Selective power delivery
- Through-wall charging
- Solar wireless transmission
Buying Guide: Best Practices
What to Look For
Essential Features:
- Qi certification
- Appropriate wattage
- Safety certifications (FCC, CE)
- Good reviews
- Warranty included
Nice-to-Have Features:
- LED indicators
- Multiple coils
- Cooling system
- Magnetic alignment
- USB pass-through
Red Flags to Avoid:
- No brand name
- Unusually cheap
- No certifications
- Poor reviews about heat
- No included adapter
Price vs. Performance
Budget ($10-20):
- Basic 5W-10W charging
- Single coil
- No frills
- Good for overnight
- Examples: Anker PowerWave, TOZO W1
Mid-Range ($20-50):
- 10W-15W charging
- Better build quality
- Some features
- Brand reputation
- Examples: Belkin Boost, Samsung Wireless Charger
Premium ($50-150):
- Fast charging
- Multiple devices
- Premium materials
- Advanced features
- Examples: Apple MagSafe, Nomad Base Station
Brand Recommendations
Most Reliable:
- Anker: Great value, good warranty
- Belkin: Apple partnership, quality
- Samsung: Good for Android
- Mophie: Premium quality
- RAVPower: Feature-rich
Best for iPhone:
- Apple MagSafe
- Belkin MagSafe
- Anker MagSafe
- Mophie MagSafe
Best for Android:
- Samsung official chargers
- Google Pixel Stand
- OnePlus Warp Charge
- Anker PowerWave
Conclusion: Is Wireless Charging Worth It?
Wireless charging has evolved from a gimmick to a genuine convenience that millions rely on daily. While it’s not perfect – slower than wired, less efficient, and position-dependent – the convenience factor often outweighs these drawbacks for many users.
Wireless Charging Is Worth It If:
- You charge overnight regularly
- You value convenience over speed
- You’ve had issues with charging ports
- You have multiple Qi devices
- You want a cleaner setup
Stick with Wired Charging If:
- You need fastest possible charging
- You’re very energy conscious
- You use phone while charging often
- You’re on a tight budget
- Your phone barely lasts a day
The Balanced Approach: Most users benefit from having both options. Use wireless charging for convenient overnight charging and desktop top-ups, but keep a fast wired charger for when you need quick power. As the technology improves, wireless charging will become faster and more efficient, but for now, it’s best viewed as a complement to, not a replacement for, traditional charging.
The physics that makes wireless charging possible has been understood for over a century, but we’re just beginning to realize its potential. As efficiency improves and range increases, wireless power could transform how we think about keeping our devices charged. Until then, understanding how it works helps you make the most of what’s available today.
